Introduction to Generation Z’s Financial Mindset
Generation Z, typically defined as individuals born between the late 1990s and early 2010s, represents a demographic that has been significantly influenced by technological advancements and economic volatility. Growing up amidst rapid digital transformation, this generation has access to a plethora of financial information at their fingertips, which shapes their perspectives on personal finance. Their comfort with technology fosters a unique financial mindset, where digital tools and financial apps become integral to their approach towards budgeting, saving, and investing.
The economic landscape during their formative years has also left a profound impact on Generation Z’s perception of finance. Witnessing the repercussions of the 2008 financial crisis and subsequent economic fluctuations, this generation harbors a cautious attitude toward debt and spending. Many Gen Z individuals prioritize financial stability and are inclined to save rather than indulge in excessive consumption, contrasting starkly with previous generations who may have demonstrated a propensity for credit use and lifestyle inflation. This pragmatic viewpoint often leads them to seek out diverse income streams, including freelance work or entrepreneurial ventures, as they strive for financial independence.
Moreover, the issue of financial literacy plays a crucial role in shaping Generation Z’s financial behaviors. Although they are resourceful in seeking information, there exists a gap in comprehensive financial education within traditional schooling systems. Consequently, many Gen Z individuals turn to online platforms for learning about personal finance, investment strategies, and debt management. Understanding these unique characteristics and challenges faced by Generation Z is vital for financial educators, institutions, and employers looking to engage this demographic effectively. The evolving financial landscape demands attention to their distinct preferences and values, forging pathways for improved financial literacy and empowerment for Generation Z.
Survey Findings: Spending Habits and Saving Trends
Recent surveys have illuminated the distinct spending habits and saving trends exhibited by Generation Z, a demographic characterized by its unique financial perspectives. One notable trend is their preference for conscious consumerism, where purchasing decisions are heavily influenced by sustainability practices. Many Gen Z individuals prioritize brands that demonstrate social responsibility and environmental stewardship, reflecting an inclination to support products that align with their values.
Furthermore, Generation Z tends to exhibit a preference for experiences over material possessions. This shift in consumer behavior marks a significant departure from the habits of previous generations, who often placed a higher value on owning tangible goods. Consequently, spending patterns are increasingly directed towards experiences such as travel, dining, and entertainment, with the understanding that these investments contribute to their personal fulfillment.
When it comes to saving behaviors, Generation Z is motivated by various factors, including education, emergency funds, and future investments. Surveys indicate that this cohort tends to save more diligently compared to Millennials at a similar age, with average savings rates reflecting a heightened awareness of financial security. Many in this generation have adopted strategic budgeting techniques, frequently employing mobile apps to assist with tracking expenses and managing their finances efficiently.
It is also important to note that financial education plays a pivotal role, as members of Generation Z often seek knowledge through digital resources, financial literacy programs, and peer discussions. This quest for information further distinguishes their approach to personal finance, exemplifying a proactive stance in directing their financial futures. Overall, the convergence of these trends illustrates a considerable shift in spending and saving behaviors, revealing the depth of Generation Z’s financial acumen and commitment to responsible finance management.
Investment Strategies and Financial Technology Usage
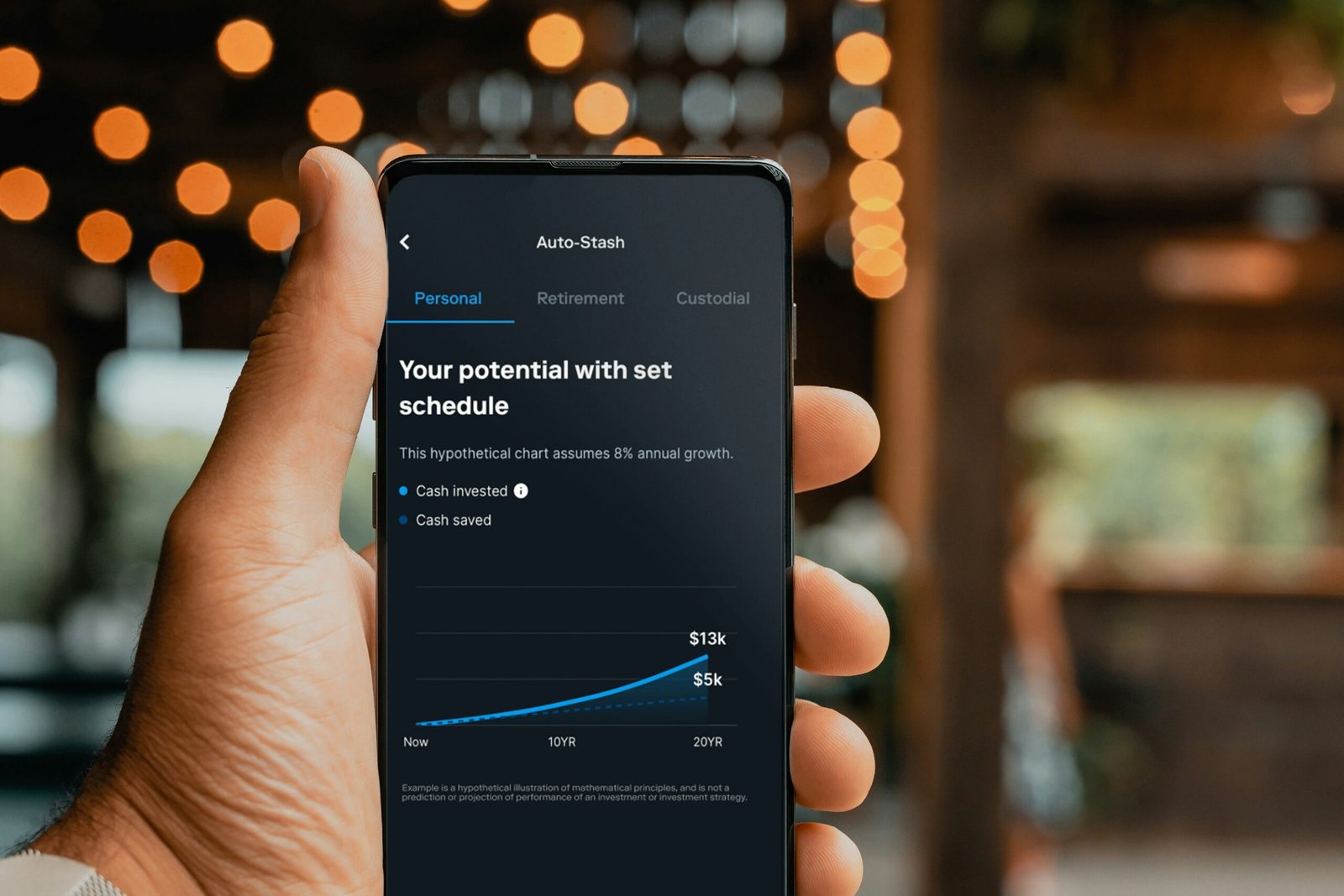
Generation Z, born roughly between 1997 and 2012, represents a unique perspective in the realm of personal finance, particularly in their investment strategies and the use of financial technology. Unlike previous generations, Gen Z has been raised in a digital environment where mobile applications and online resources greatly influence financial decision-making. These young investors are increasingly turning to mobile investing apps as their primary tool for managing investments. These platforms not only offer user-friendly interfaces but also provide real-time data and analytics, promoting ease of access to financial markets.
The emergence of cryptocurrency has further captured the interest of Generation Z, with many viewing digital currencies as a gateway to modern investment strategies. This younger demographic shows a higher propensity to invest in cryptocurrencies compared to older generations, driven by the perceived innovation and potential high returns. Reports indicate that Gen Z’s engagement with cryptocurrencies is often fueled by discussions and promotions on social media platforms, demonstrating the significant role that digital communication plays in shaping their financial choices.
Moreover, social media is a double-edged sword; while it offers opportunities for learning and sharing insights, it can also lead to misinformation and impulsive investment decisions. The influence of social media on investment trends has given rise to phenomena like meme stocks, which have become popular among young investors eager to capitalize on the latest trends. Despite their enthusiasm for these new vehicles, it’s essential to consider how well Generation Z understands traditional investments such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. While they may excel in navigating digital options, many still display a gap in knowledge regarding established wealth-building strategies, suggesting a need for enhanced financial education in this area.
Educational Resources and Future Financial Planning
Generation Z is distinct in its approach to financial literacy and planning, favoring modern educational resources that align with their technological preferences. Online courses, podcasts, and YouTube have emerged as the primary channels for acquiring personal finance knowledge among this cohort. These platforms offer flexible, engaging, and easily accessible information, enabling individuals to learn at their own pace. For instance, many popular personal finance YouTubers simplify complex topics, making it easier for Gen Z to understand budgeting, saving, and investing concepts.
In contrast to more traditional financial education methods, such as classroom lectures or textbooks, these contemporary resources often resonate more with Generation Z, who are accustomed to rapid information consumption and interactive formats. Additionally, online courses often include visual aids and practical exercises, which enhance learning and retention. This shift points to a need for educational institutions and financial organizations to adapt their methods to cater to Gen Z’s preferences, ensuring that financial literacy initiatives are relevant and appealing.
In terms of long-term financial goals, Generation Z is particularly focused on financial independence and security. Many are drawn to entrepreneurship and innovative career paths, reflecting a desire to take control of their financial destinies. This demographic often emphasizes the importance of building multiple income streams, saving for emergencies, and investing early to secure a robust financial future. As they continue to navigate economic uncertainties, their commitment to financial education is paramount.
Understanding Generation Z’s evolving preferences for financial literacy resources and their aspirations can provide critical insights for educators, financial institutions, and policymakers. By embracing technology and contemporary teaching methods, they can better equip this generation to manage their finances effectively and achieve their future financial goals.