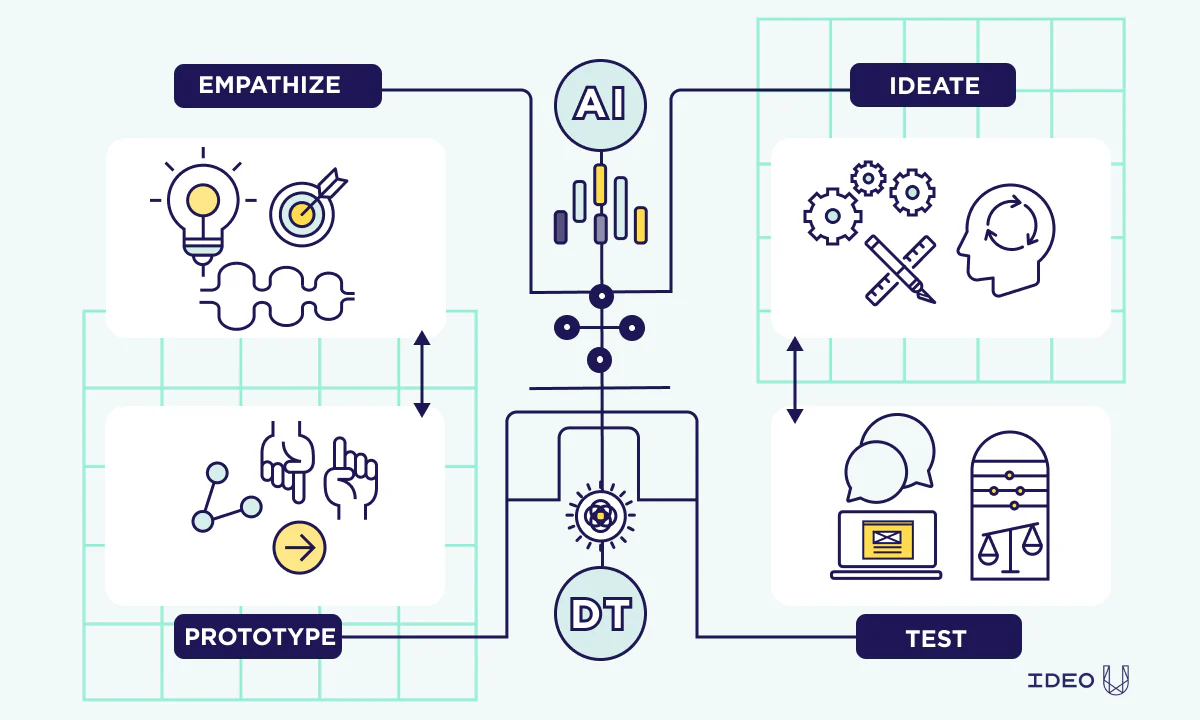
Introduction to AI Tools in Design
Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools have emerged as transformative agents in the field of design, creating a paradigm shift in how designers approach their work. Over recent years, these tools have evolved significantly, transitioning from simple automation to sophisticated systems capable of complex functionalities. The integration of AI technology into design processes has facilitated numerous enhancements, making tasks more efficient and enabling designers to explore new creative possibilities.
AI tools currently being employed in design encompass various applications, such as generative design software, image recognition technology, and predictive analytics. Generative design algorithms, for instance, allow designers to input specific parameters and receive a multitude of design options, thereby reducing the time spent on brainstorming and concept development. This capability not only optimizes the design workflow but also fosters innovation by enabling exploration beyond traditional design limits.
Moreover, AI-driven image recognition tools assist designers in identifying trends and patterns by analyzing vast datasets. This analysis can influence decision-making by providing insights into consumer preferences and behaviors. Predictive analytics further enhance this capability by forecasting future market demands and trends, helping designers align their projects with anticipated needs. The utilization of these AI tools is markedly changing the design landscape, leading to more informed, data-driven approaches.
The implications of AI technology for designers are both profound and multifaceted. On one hand, these tools improve overall efficiency, allowing designers to allocate time and resources more effectively. On the other hand, they open avenues for creative exploration, encouraging designers to push the boundaries of what is possible. As we delve deeper into the survey findings, these themes will be further examined, revealing the intricate dynamics between AI technology and its impact on the design profession.
Methodology of the Survey
The methodology employed in this survey aimed to gather comprehensive data on designers’ perspectives regarding AI tools. The target demographics consisted of professional designers across various fields, including graphic design, product design, and fashion design. To ensure a diverse representation of opinions, participants were selected from multiple geographic locations and industry backgrounds, promoting a well-rounded understanding of designer views on artificial intelligence applications.
The survey sample size comprised 500 designers, selected through a combination of convenience and purposive sampling methods. This size was deemed sufficient to achieve statistically relevant results while providing a variety of insights drawn from different design disciplines. The survey was conducted online, facilitating easy access for participants and encouraging a higher response rate. This approach not only streamlined data collection but also allowed designers to complete the survey at their convenience, thereby increasing the likelihood of thoughtful, reflective responses.
The survey format included a mix of quantitative and qualitative questions. Quantitative questions utilized scaled responses, allowing participants to express their level of agreement or satisfaction with different aspects of AI tools using a Likert scale. Qualitative questions encouraged designers to elaborate on their experiences and opinions, providing rich narrative data that complemented the numerical findings. The combination of these question types helped to reveal both statistical patterns and nuanced insights into designer attitudes.
Data analysis involved both descriptive and inferential statistical techniques for the quantitative responses, while thematic analysis was employed for qualitative responses. This dual approach ensured that the findings were not only reliable but also reflective of the complex nature of designers’ experiences with AI tools. The overall methodology was designed to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the key trends and patterns, fostering informed discussions around the implications of AI in design.
Key Findings from Designer Perspectives
The survey conducted among designers provided compelling insights into their perspectives on AI tools. A significant proportion of respondents, approximately 68%, expressed a positive attitude towards the integration of artificial intelligence into their design processes. Designers noted that AI tools could enhance creativity and efficiency, streamlining repetitive tasks and freeing up time for more meaningful creative exploration. In particular, graphic designers highlighted how AI-driven design automation might reduce the workload associated with routine designs, allowing them to focus on conceptual development.
However, alongside these benefits, challenges associated with AI adoption were also prevalent in the responses. About 45% of designers raised concerns about the potential for AI tools to compromise the authenticity of creative work. There were fears that reliance on technology could diminish individual creativity and unique design perspectives. Moreover, participants reported feeling uncertain about the reliability of AI-generated designs, especially in fields like UX/UI design, where user experience and empathy are critical components.
Interestingly, the level of comfort with AI tools varied considerably based on design discipline and experience level. For instance, younger designers, particularly those in the tech-savvy UX/UI realm, showed greater openness to leveraging AI, often viewing it as a necessary evolution in their creative toolkit. In contrast, more seasoned graphic designers tended to be more cautious, with many expressing a preference for traditional methods over new technologies. Geographical context also played a role; designers based in urban innovation hubs generally exhibited a more favorable attitude towards AI compared to their counterparts in less tech-centric locales.
These findings illustrate a complex landscape where enthusiasm for AI tools coexists with skepticism. As designers navigate the integration of these technologies, the ongoing dialogue around the intersection of creativity and machine-generated content will be essential in shaping the future of design practice.
Implications and Future Directions
The survey findings present significant implications for the design industry, shedding light on the evolving relationship between designers and AI tools. As the capabilities of artificial intelligence continue to advance, the integration of these technologies into design practice is becoming increasingly essential. Designers must adapt to these changes and explore how AI can enhance creativity, streamline workflows, and assist in decision-making processes while maintaining a human-centric approach to design.
One potential pathway for the integration of AI into design practice involves incorporating AI-driven tools into the initial stages of the design process. This could facilitate idea generation, allowing designers to explore a broader range of concepts quickly. By leveraging AI algorithms to analyze trends or predict user preferences, designers can make more informed choices, ultimately resulting in more effective and relevant output. However, this necessitates a profound understanding of AI capabilities and limitations, indicating a clear need for educational frameworks to evolve in tandem with technological advancements.
Education and training programs within design institutions must address the increasing prominence of AI. Curricula should include comprehensive insights into AI technologies, exploring their functionalities, ethical considerations, and potential applications in design projects. By equipping future designers with the necessary skills and knowledge, educators can prepare them for a landscape where human creativity and AI tools complement each other, rather than compete. Furthermore, ongoing dialogues among designers, educators, and industry stakeholders are paramount in exploring the impact of AI on creativity and job roles. Such discussions can foster a community that values innovation while being mindful of the social and ethical implications of AI’s growing presence in the field.
In conclusion, engaging thoughtfully with AI technologies presents an opportunity for the design industry to redefine creative processes. By embracing innovation, prioritizing education, and maintaining an open dialogue, industry professionals can navigate the future of design with clarity and purpose.